Euler Characteristic Curve Vectorization of Persistent Homology
Source:R/zzz-step-vpd-euler-characteristic-curve.R
step_vpd_euler_characteristic_curve.RdThe function step_vpd_euler_characteristic_curve() creates
a specification of a recipe step that will convert
a list-column of 3-column matrices of persistence data
to a list-column of 1-row matrices of vectorizations.
Usage
step_vpd_euler_characteristic_curve(
recipe,
...,
role = "predictor",
trained = FALSE,
xseq = NULL,
xmin = NULL,
xmax = NULL,
xlen = NULL,
xby = NULL,
max_hom_degree = Inf,
evaluate = "intervals",
columns = NULL,
keep_original_cols = TRUE,
skip = FALSE,
id = rand_id("vpd_euler_characteristic_curve")
)Arguments
- recipe
A recipe object. The step will be added to the sequence of operations for this recipe.
- ...
One or more selector functions to choose variables for this step. See
selections()for more details.- role
For model terms created by this step, what analysis role should they be assigned? By default, the new columns created by this step from the original variables will be used as predictors in a model.
- trained
A logical to indicate if the quantities for preprocessing have been estimated.
- xseq
A discretization grid, as an increasing numeric vector.
xseqoverrides the otherx*parameters with a warning.- xmin, xmax, xlen, xby
Limits and resolution of a discretization grid; specify only one of
xlenandxby.- max_hom_degree
The highest degree, starting from 0, of the features to be transformed.
- evaluate
The method by which to vectorize continuous functions over a grid, either 'intervals' or 'points'. Some functions only admit one method.
- columns
A character string of the selected variable names. This field is a placeholder and will be populated once
prep()is used.- keep_original_cols
A logical to keep the original variables in the output. Defaults to
FALSE.- skip
A logical. Should the step be skipped when the recipe is baked by
bake()? While all operations are baked whenprep()is run, some operations may not be able to be conducted on new data (e.g. processing the outcome variable(s)). Care should be taken when usingskip = TRUEas it may affect the computations for subsequent operations.- id
A character string that is unique to this step to identify it.
Value
An updated version of recipe with the new step added to the
sequence of any existing operations.
Details
Persistent homology is usually encoded as birth–death pairs (barcodes or diagrams), but the space of persistence data sets does not satisfy convenient statistical properties. Such applications as hypothesis testing and machine learning benefit from transformations of persistence data, often to Hilbert spaces (vector spaces with inner products and induced metrics).
Engine
The Euler characteristic curve vectorization deploys
TDAvec::computeEulerCharacteristic().
See there for definitions and references.
Tuning Parameters
This step has 1 tuning parameter:
max_hom_degree: Highest homological degree (type: integer, default:Inf)
Examples
library(recipes)
# inspect vectorized features
volc_dat <- data.frame(image = I(list(volcano / 10)))
recipe(~ image, data = volc_dat) %>%
step_pd_raster(image, method = "link_join") %>%
step_vpd_euler_characteristic_curve(image, max_hom_degree = 2) %>%
print() -> volc_rec
#>
#> ── Recipe ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#>
#> ── Inputs
#> Number of variables by role
#> predictor: 1
#>
#> ── Operations
#> • persistent features from a cubical filtration of: image
#> • Euler characteristic curve of: image
print(volc_rec)
#>
#> ── Recipe ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#>
#> ── Inputs
#> Number of variables by role
#> predictor: 1
#>
#> ── Operations
#> • persistent features from a cubical filtration of: image
#> • Euler characteristic curve of: image
volc_rec %>%
prep(training = volc_dat) %>%
bake(new_data = volc_dat)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 100
#> image image_ec_1 image_ec_2 image_ec_3 image_ec_4 image_ec_5 image_ec_6
#> <list> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 <PHom> 0 0 0 0 0 0
#> # ℹ 93 more variables: image_ec_7 <dbl>, image_ec_8 <dbl>, image_ec_9 <dbl>,
#> # image_ec_10 <dbl>, image_ec_11 <dbl>, image_ec_12 <dbl>, image_ec_13 <dbl>,
#> # image_ec_14 <dbl>, image_ec_15 <dbl>, image_ec_16 <dbl>, image_ec_17 <dbl>,
#> # image_ec_18 <dbl>, image_ec_19 <dbl>, image_ec_20 <dbl>, image_ec_21 <dbl>,
#> # image_ec_22 <dbl>, image_ec_23 <dbl>, image_ec_24 <dbl>, image_ec_25 <dbl>,
#> # image_ec_26 <dbl>, image_ec_27 <dbl>, image_ec_28 <dbl>, image_ec_29 <dbl>,
#> # image_ec_30 <dbl>, image_ec_31 <dbl>, image_ec_32 <dbl>, …
# dimension-reduce using vectorized features
data(permeability_qsar, package = "modeldata")
permeability_qsar %>%
transform(perm_cut = cut(permeability, breaks = seq(0, 60, 10))) %>%
subset(select = -permeability) %>%
tidyr::nest(chem_fp = -perm_cut) %>%
print() -> perm_dat
#> # A tibble: 6 × 2
#> perm_cut chem_fp
#> <fct> <list>
#> 1 (10,20] <tibble [20 × 1,107]>
#> 2 (0,10] <tibble [110 × 1,107]>
#> 3 (20,30] <tibble [7 × 1,107]>
#> 4 (30,40] <tibble [8 × 1,107]>
#> 5 (40,50] <tibble [16 × 1,107]>
#> 6 (50,60] <tibble [4 × 1,107]>
recipe(perm_cut ~ chem_fp, data = perm_dat) %>%
step_pd_point_cloud(chem_fp, max_hom_degree = 2) %>%
step_vpd_euler_characteristic_curve(chem_fp, max_hom_degree = 2) %>%
step_pca(starts_with("chem_fp_"), num_comp = 2) %>%
print() -> perm_rec
#>
#> ── Recipe ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#>
#> ── Inputs
#> Number of variables by role
#> outcome: 1
#> predictor: 1
#>
#> ── Operations
#> • persistent features from a Rips filtration of: chem_fp
#> • Euler characteristic curve of: chem_fp
#> • PCA extraction with: starts_with("chem_fp_")
perm_est <- prep(perm_rec, training = perm_dat)
perm_res <- bake(perm_est, new_data = perm_dat)
# inspect results
tidy(perm_rec)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 6
#> number operation type trained skip id
#> <int> <chr> <chr> <lgl> <lgl> <chr>
#> 1 1 step pd_point_cloud FALSE FALSE pd_point_cloud_…
#> 2 2 step vpd_euler_characteristic_curve FALSE FALSE vpd_euler_chara…
#> 3 3 step pca FALSE FALSE pca_a0FWR
tidy(perm_rec, number = 2)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> terms value id
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 chem_fp NA vpd_euler_characteristic_curve_rUlDf
tidy(perm_est, number = 2)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> terms value id
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 chem_fp NA vpd_euler_characteristic_curve_rUlDf
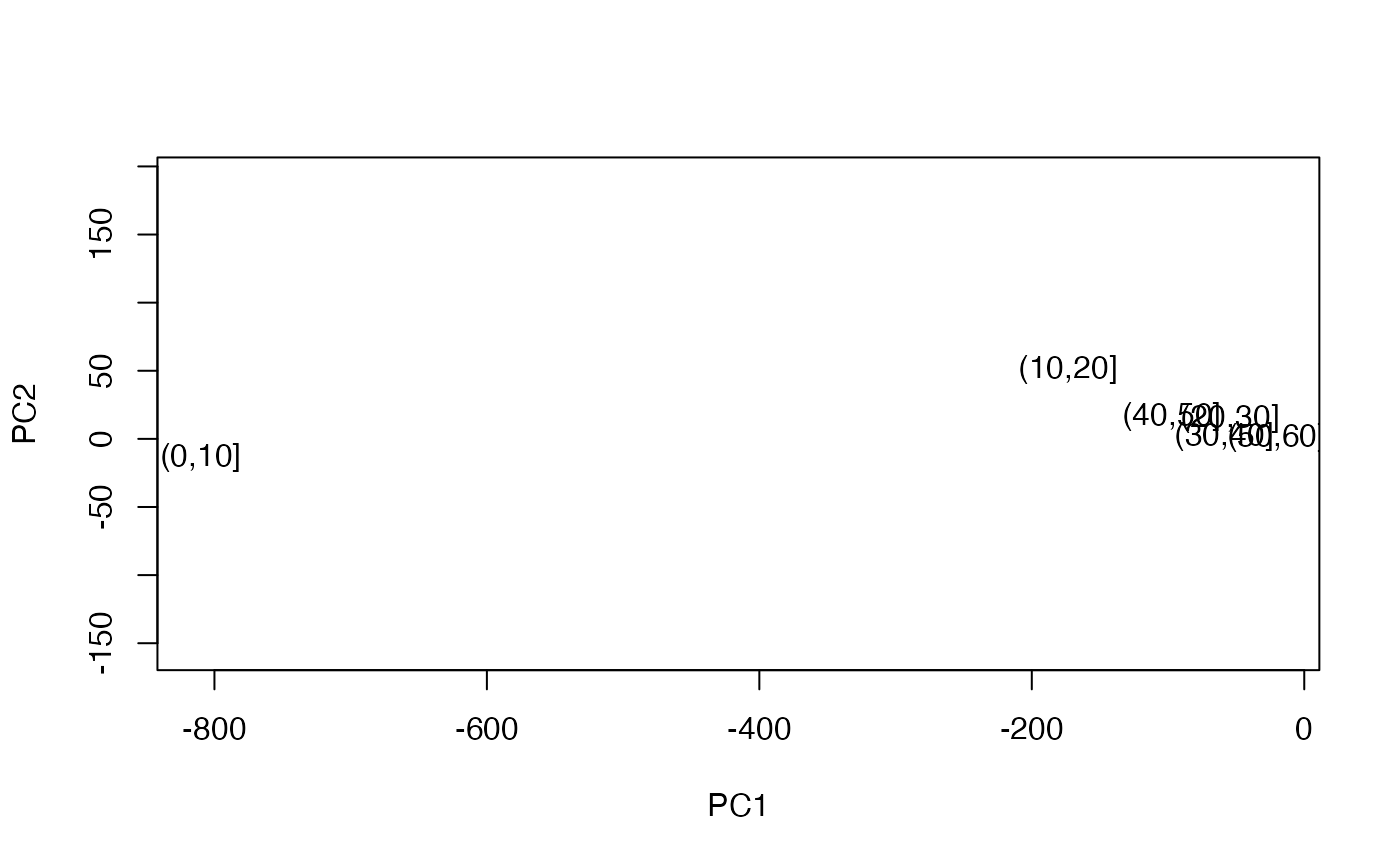
# visualize results
with(perm_res, {
plot(PC1, PC2, type = "n", asp = 1)
text(PC1, PC2, labels = perm_cut)
})